Natural Language Processing (NLP) has witnessed remarkable advancements in recent years, primarily due to the development of transformer models. These models, particularly the groundbreaking Transformer architecture, have revolutionized various NLP tasks, including machine translation, language understanding, and text generation. In this article, we explore seven significant developments in transformer model development that have paved the way for the current state-of-the-art NLP systems.
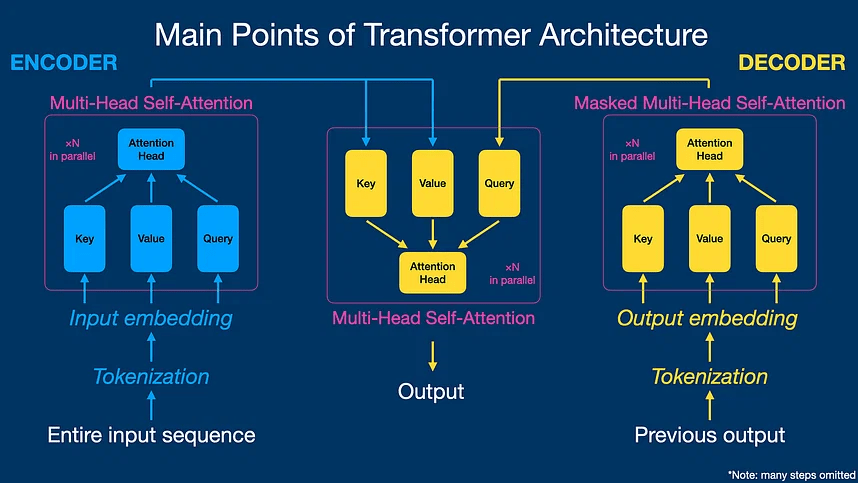
- Transformer Architecture: The Transformer architecture, introduced in 2017 by Vaswani et al., marked a significant shift in NLP. Unlike traditional recurrent neural networks, Transformers utilize self-attention mechanisms to process sequences in parallel, eliminating the need for sequential processing. This parallelization significantly improves computational efficiency and allows for better long-range dependencies modeling.
- BERT: Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) is a transformer-based model introduced by Google in 2018. It pretrains a deep bidirectional representation on a large corpus and demonstrates impressive performance across various NLP tasks. BERT’s contextualized word embeddings capture the meaning of words based on their surrounding context, resulting in a leap forward in natural language understanding.
- GPT: The Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT) series, pioneered by OpenAI, encompasses a family of models with increasing sizes and capabilities. GPT-3, released in 2020, consists of a staggering 175 billion parameters and achieves state-of-the-art results in numerous language generation tasks. GPT models employ a decoder-only transformer architecture, making them highly proficient in generating coherent and contextually appropriate text.
- XLNet: XLNet, proposed by Yang et al. in 2019, introduces a new permutation-based training objective that overcomes the limitations of the traditional auto-regressive language modeling objective used in models like GPT. By modeling the probability distribution over all possible permutations of the input sequence, XLNet captures bidirectional dependencies more effectively, achieving superior performance in tasks requiring contextual understanding.
- T5: Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer (T5) is a versatile transformer model introduced by Google in 2019. T5 aims to unify diverse NLP tasks under a single framework, using a text-to-text approach where all tasks are converted into a text generation task. By training on a large-scale dataset with multiple tasks, T5 demonstrates impressive performance on a wide range of NLP benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art results.
- ALBERT: A Lite BERT (ALBERT) addresses the limitations of BERT’s large memory footprint by introducing parameter reduction techniques. ALBERT achieves comparable performance to BERT while significantly reducing the model size, making it more efficient for deployment on resource-constrained devices. By sharing parameters across layers, ALBERT demonstrates remarkable compression without sacrificing performance.
- ViT: Vision Transformer (ViT) represents an extension of transformer models from NLP to computer vision tasks. ViT applies self-attention mechanisms to image patches, breaking down images into sequences for processing. This approach eliminates the need for handcrafted features or convolutional neural networks, achieving impressive results in image classification and other vision tasks.
To Learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/transformer-model-development-services/