In recent years, deep learning models have revolutionized various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, such as machine translation, text generation, and sentiment analysis. The Transformer model, introduced by Vaswani et al. in 2017, marked a significant advancement in NLP with its attention mechanism, allowing it to process long-range dependencies efficiently. Building upon this success, researchers have further enhanced the Transformer architecture to tackle more complex tasks. One such extension is the Action Transformer model, which aims to incorporate dynamic action generation into the standard Transformer framework.
The Evolution of Transformers
Before delving into the specifics of an Action Transformer, let’s briefly recap the original Transformer model’s key components. The Transformer architecture is based on an encoder-decoder framework, where the encoder processes the input sequence, and the decoder generates the output sequence. It utilizes self-attention mechanisms, allowing each word to attend to all other words in the sequence, enabling parallel processing and capturing contextual information effectively.
Understanding Action Transformer Model
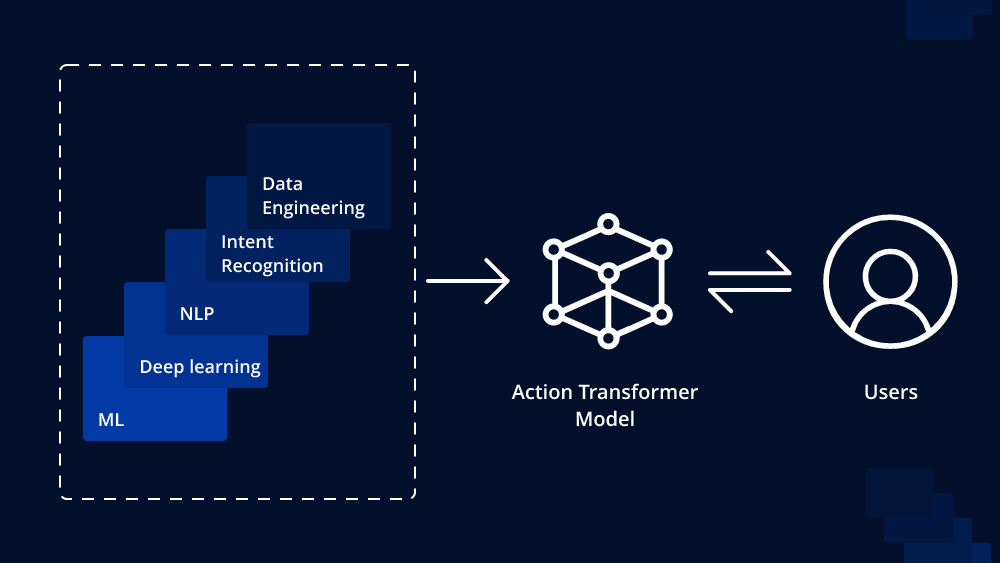
The Action Transformer model extends the traditional Transformer by introducing a dynamic action generation mechanism. Unlike standard Transformers, which are primarily used for sequence-to-sequence tasks like machine translation, Action Transformers excel in tasks where the output is not a fixed sequence but depends on the model’s actions during the generation process.
The concept of actions in an Action Transformer refers to the decisions made by the model during the decoding process. Instead of straightforwardly predicting each token in a sequential manner, the model actively selects actions that influence subsequent generations. This dynamic decision-making allows the Action Transformer to exhibit a more interactive and adaptive behavior during sequence generation.
How does an Action Transformer work?
- Action Space Definition: In an Action Transformer, the first step involves defining an action space. This space comprises a set of possible actions the model can take at each generation step. Actions can range from selecting a particular token from the vocabulary to applying various transformation operations on the current hidden state.
- Action Selection: During the decoding process, the Action Transformer chooses actions at each time step based on the context, current hidden state, and predefined action space. The model can also learn to assign probabilities to different actions, allowing it to make informed decisions during generation.
- Action Execution and Generation: After selecting an action, the Action Transformer performs the chosen action, which might involve appending a token to the output sequence or modifying the hidden state. The model then proceeds to the next generation step, and the process iterates until the desired sequence is generated or a predefined stopping condition is met.
- Feedback Loop: One key aspect of the Action Transformer is its ability to receive feedback on the impact of previously selected actions. This feedback loop enables the model to learn from its past decisions and adjust its behavior accordingly. Reinforcement learning techniques are often employed to optimize action selection policies based on the generated sequences’ quality.
Applications of Action Transformer Models
Action Transformer models have demonstrated their effectiveness in various NLP tasks, particularly those with complex and dynamic output generation requirements. Some prominent applications include:
- Dialogue Systems: Action Transformers are well-suited for building interactive dialogue systems, where the model engages in dynamic conversation and adapts its responses based on the user’s input.
- Code Generation: In programming-related tasks, Action Transformers can generate code snippets step-by-step, ensuring that each action taken is syntactically and semantically correct.
- Image Captioning: When generating captions for images, an Action Transformer can dynamically adjust the description based on the visual content and the generated text so far.
Conclusion
The Action Transformer model represents a significant advancement in sequence generation tasks within the NLP domain. By incorporating dynamic action selection and feedback mechanisms, the model gains the ability to make interactive and adaptive decisions during sequence generation. As researchers continue to explore and refine this architecture, we can expect Action Transformers to find broader applications in various real-world scenarios, further pushing the boundaries of natural language processing capabilities.
To Learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/action-transformer-model/