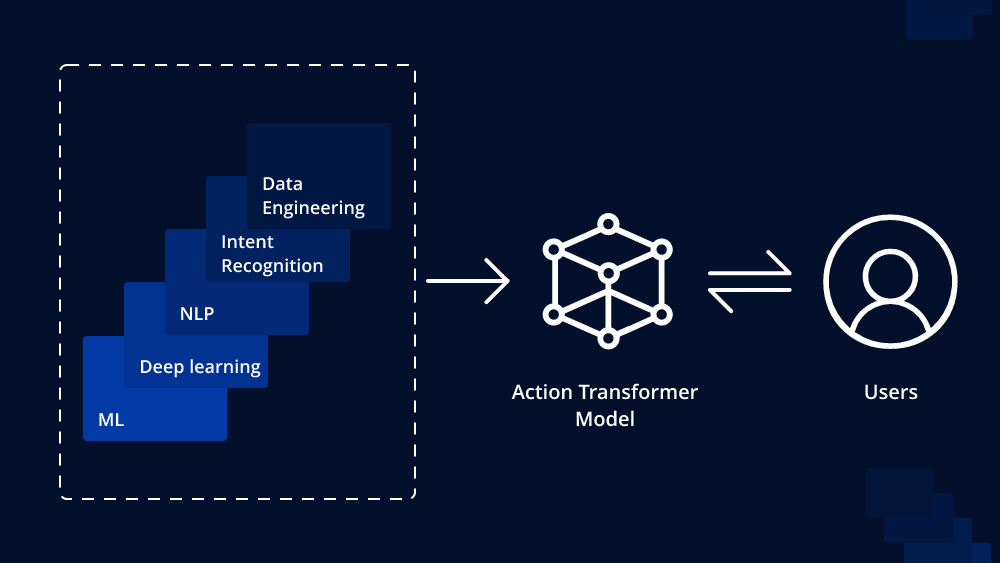
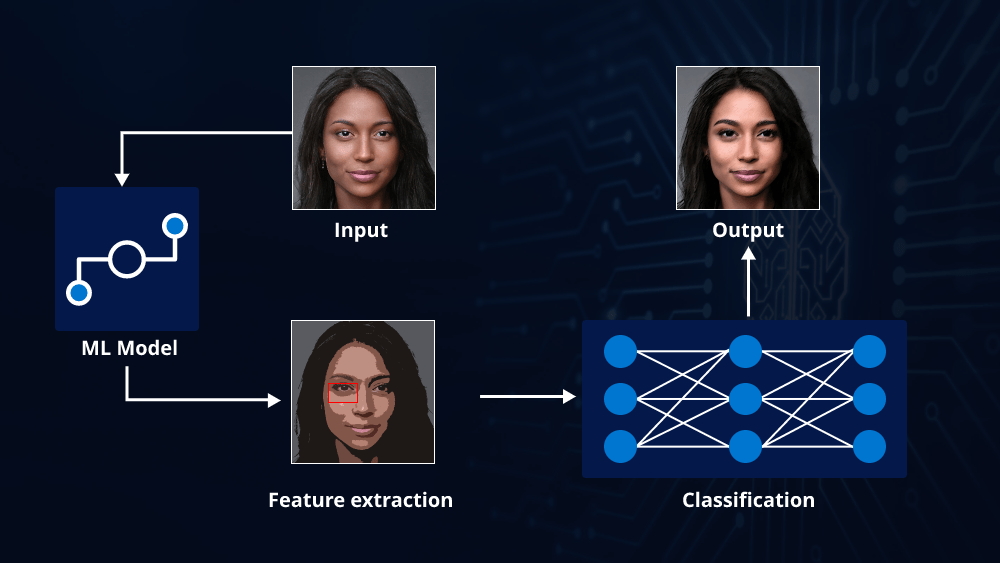
The Transformer model, introduced by Vaswani et al. in 2017, revolutionized natural language processing tasks and brought significant advancements in various AI fields. It uses a self-attention mechanism to process input sequences and capture long-range dependencies effectively. However, as machine learning models have evolved, researchers have explored ways to make Transformers more powerful and efficient.

One such advancement is the Decision Transformer, a variant of the Transformer architecture that incorporates decision-making capabilities. The Decision Transformer extends the traditional self-attention mechanism to include explicit handling of decisions and outcomes, making it well-suited for tasks that involve sequential decision-making. In this article, we will explore how to use the Decision Transformer in a Transformer for various applications.
Understanding the Decision Transformer
The Decision Transformer builds upon the standard Transformer model and introduces additional components to handle decisions during sequence processing. It incorporates decision heads that can influence the model’s behavior based on prior outcomes. This allows the Decision Transformer to excel in tasks with multiple decision points and conditional dependencies.
Step 1: Model Architecture
The first step in using the Decision Transformer is to understand its architecture. Like the original Transformer, it consists of an encoder-decoder architecture with self-attention layers. However, the Decision Transformer extends this by adding decision heads to the self-attention mechanism. These decision heads take into account the decisions made at each step and use this information to guide the model’s future decisions.
Step 2: Data Preparation
Before using the Decision Transformer, ensure that your data is appropriately prepared for the specific task you want to tackle. For sequential decision-making tasks, the dataset should include examples with decision points and corresponding outcomes. Each decision point should be associated with a specific token in the input sequence.
Step 3: Implementing Decision Heads
To incorporate decision-making capabilities, you need to modify the self-attention mechanism of the Transformer. In each self-attention layer, decision heads are introduced to capture the decisions made at each step. These decision heads take the form of additional attention mechanisms that consider the previous decisions and their outcomes.
Step 4: Training the Model
Once the Decision Transformer is implemented, the next step is to train the model on your prepared dataset. During training, the model learns to make decisions based on the provided outcomes at each decision point. This process helps the model develop a deeper understanding of conditional dependencies and improves its sequential decision-making capabilities.
Step 5: Evaluation and Fine-Tuning
After training the Decision Transformer, evaluate its performance on the task at hand. The evaluation metrics will depend on the specific application, but they should take into account both the accuracy of decisions and the overall task performance.
If the model’s performance is not satisfactory, consider fine-tuning it on additional data or adjusting hyperparameters to improve its decision-making abilities.
Applications of Decision Transformers
Decision Transformers find applications in various fields due to their ability to handle sequential decision-making tasks effectively. Some notable applications include:
- Autonomous Systems: Decision Transformers can be used in autonomous vehicles and robots, enabling them to make complex decisions in real-time based on sensor inputs and prior outcomes.
- Financial Modeling: In finance, Decision Transformers can aid in making investment decisions by considering historical outcomes and market conditions.
- Medical Diagnosis: Decision Transformers can be employed in medical diagnosis systems, taking into account patient history and test results to arrive at accurate diagnoses.
- Natural Language Processing: In NLP, Decision Transformers can be used for tasks involving multiple decision points, such as dialogue generation and question-answering systems.
Conclusion
The Decision Transformer extends the capabilities of the traditional Transformer model by incorporating decision-making mechanisms. By explicitly considering decisions and outcomes, the Decision Transformer is well-suited for tasks that involve sequential decision-making. When applied to various applications, Decision Transformers have the potential to improve performance and enhance the decision-making abilities of AI systems, making them a valuable tool in the field of machine learning.
To Learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/decision-transformer/