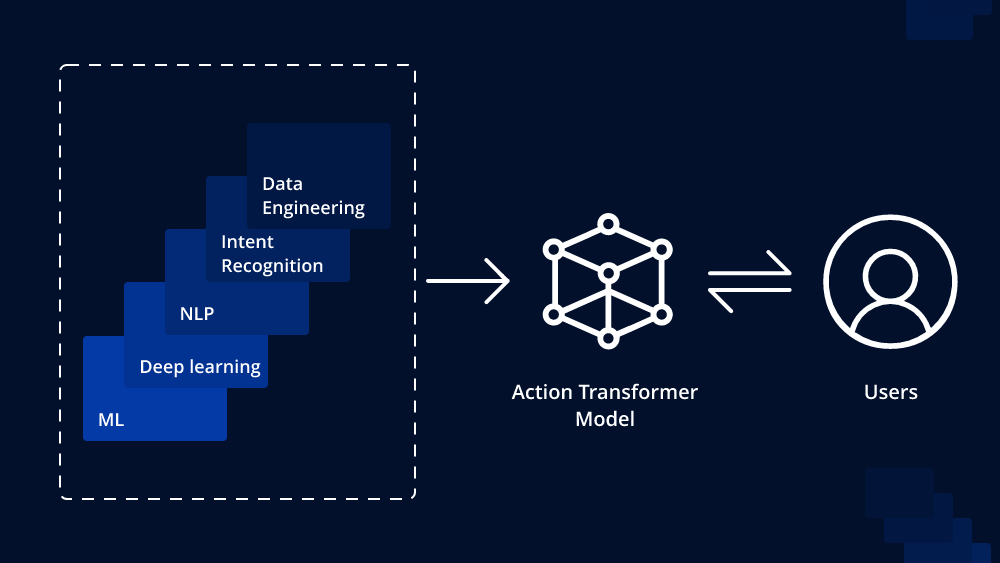
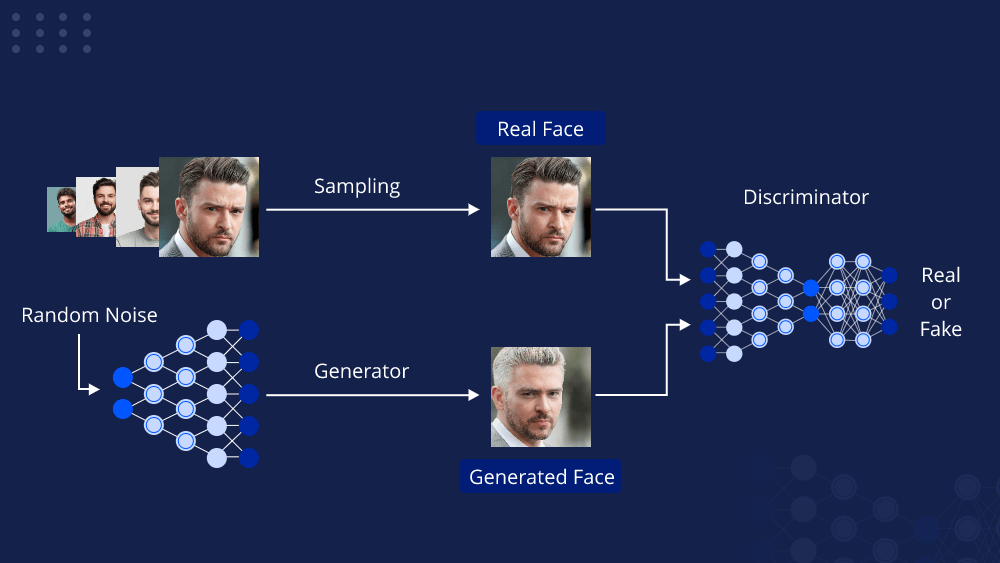
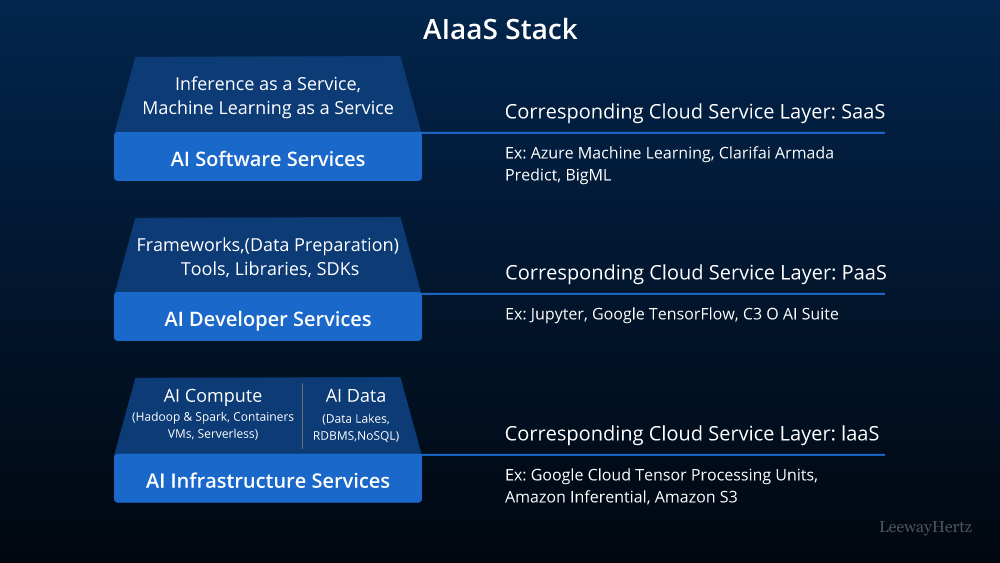
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are constantly seeking ways to leverage the power of machine learning to gain a competitive edge. However, the journey from building a machine learning model to deploying it into production can be fraught with challenges. This is where MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) pipelines come into play, acting as a bridge that connects the worlds of data science and deployment, ensuring smooth and efficient model deployment and management. In this article, we will explore the concept of MLOps pipelines, their significance, and how they can revolutionize the way machine learning models are developed and deployed.
The Need for MLOps Pipeline
Traditionally, the process of developing and deploying machine learning models has been fragmented and time-consuming. Data scientists focus on building and fine-tuning models, while DevOps teams handle deployment and operational tasks. This separation often leads to communication gaps, slow deployment cycles, and challenges in monitoring and maintaining models in production.
MLOps pipelines address these issues by integrating the development and deployment processes into a single, streamlined workflow. This approach enables organizations to:
- Foster Collaboration: MLOps encourages collaboration between data scientists, engineers, and DevOps teams. By bringing these teams together, organizations can leverage diverse expertise to build robust and reliable machine learning solutions.
- Automate and Standardize: Automation is at the core of MLOps pipelines. They enable the automation of repetitive tasks such as data preprocessing, model training, and deployment, reducing human errors and increasing efficiency. Standardization ensures that the entire process adheres to best practices and compliance requirements.
- Accelerate Deployment: MLOps pipelines reduce the time it takes to move a model from development to production. This speed is crucial in industries where timely insights from data can lead to a competitive advantage.
- Enhance Monitoring and Governance: Once a model is in production, MLOps pipelines provide mechanisms for real-time monitoring, logging, and governance. This ensures that models perform as expected and are compliant with regulations.
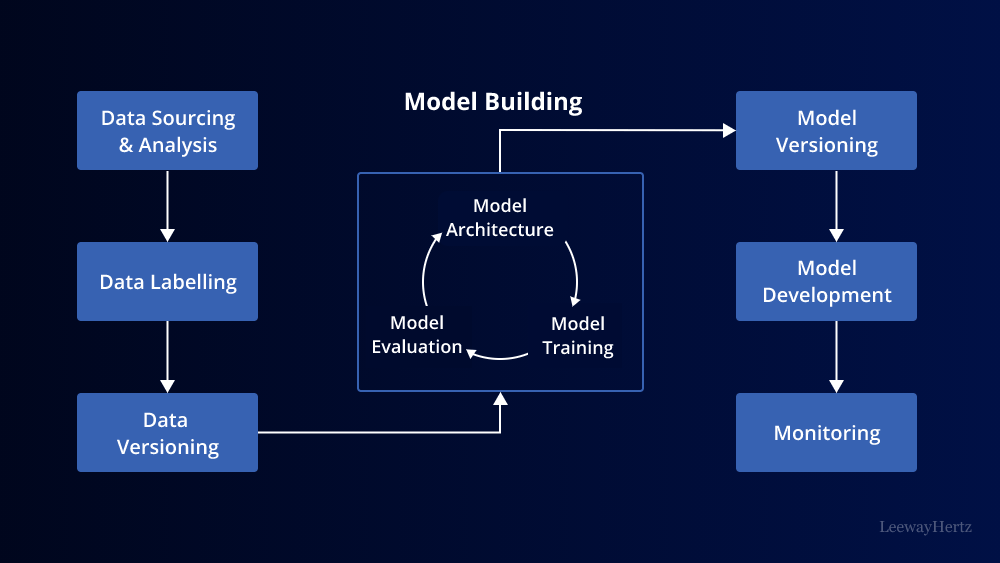
Components of an MLOps Pipeline
An MLOps pipeline consists of several key components:
- Data Ingestion: The pipeline starts with data ingestion, where raw data is collected and prepared for processing. This stage involves data cleaning, transformation, and validation.
- Model Development: Data scientists build and fine-tune machine learning models using the prepared data. This phase includes feature engineering, hyperparameter tuning, and model evaluation.
- Model Deployment: Once a model is trained and validated, it is deployed to a production environment. This stage involves containerization, scaling, and orchestration.
- Monitoring and Logging: Continuous monitoring of the deployed model’s performance is crucial. This component tracks metrics, logs, and alerts to detect anomalies and ensure the model operates as intended.
- Feedback Loop: MLOps pipelines include mechanisms for collecting feedback from the deployed model. This feedback helps data scientists improve the model over time by retraining it with new data.
- Governance and Compliance: Ensuring that models adhere to regulatory and compliance standards is essential. MLOps pipelines provide features for model governance and auditability.
Benefits of MLOps Pipeline
Implementing MLOps pipelines offers several benefits to organizations:
- Improved Efficiency: Automation reduces manual intervention, streamlining the process from data ingestion to deployment. This leads to faster model delivery and increased productivity.
- Consistency: MLOps pipelines enforce best practices and consistency in model development and deployment, reducing errors and ensuring reliability.
- Scalability: Organizations can easily scale their machine learning operations to handle larger datasets and more complex models.
- Cost Reduction: Automation and efficient resource allocation can lead to cost savings by optimizing infrastructure usage.
- Enhanced Collaboration: MLOps encourages cross-functional teams to work together, fostering a culture of collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Challenges and Considerations
While MLOps pipelines offer significant advantages, they also come with challenges. Some common considerations include:
- Data Quality: Garbage in, garbage out. Ensuring data quality is a fundamental concern as the pipeline heavily relies on the quality of the input data.
- Model Governance: Compliance and ethics in machine learning are critical. Organizations must establish robust governance processes to mitigate risks.
- Infrastructure Complexity: Setting up and maintaining the necessary infrastructure for MLOps can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Skill Gap: MLOps requires expertise in both data science and DevOps, which can be a challenge for organizations lacking such talent.
Conclusion
MLOps pipelines represent a pivotal advancement in the field of machine learning. They bridge the gap between data science and deployment, providing a structured and automated approach to developing, deploying, and managing machine learning models. By adopting MLOps practices, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data science initiatives, accelerating model deployment, improving efficiency, and ensuring compliance with regulations. As the demand for machine learning solutions continues to grow, MLOps pipelines are poised to play a central role in shaping the future of AI-driven innovation.